Understand dyestuff knowledge, delivery problem
Principles and basic principles of color matching for dyeing and proofing
Color matching is a complicated, detailed and important task. In addition to the basic color knowledge and keen color discrimination ability, proofing personnel should also master the basic principles and rules of color matching, and pay attention to the continuous accumulation of proofing materials and experience.
First, the principle of color matching
Color matching is based on the principle of "subtraction" color mixing. In practice, because the ideal three primary colors cannot be found, red, yellow, and blue are often used as substitute primary colors (also called primary colors). If you mix two different primary colors, you can get secondary colors such as orange, green, and purple; if you mix two different secondary colors, or if you mix any one of the primary colors with gray, you can get three colors . The color matching results are as follows:
Second, the basic principles of color matching
The process of color matching is relatively complicated. In order to achieve the desired results, fast, accurate and economical, the following principles should be followed:
1. "Similarity" principle
Refers to the dyeing properties of color-matching dyes as close as possible. Dyeing properties of the dye include affinity, dyeing rate, dyeing temperature, leveling property, and dyeing fastness. When color matching, try to choose the same application of large and small dyes. Otherwise, the dyeing process is difficult to formulate, and due to the poor compatibility of the dye, the color light is not easy to control, and the leveling property is poor. The three primary colors of various types of dyes are often screened dyes with excellent application performance and good compatibility, so priority should be given to color selection.
2. The "small amount" principle
When referring to color-matching (especially bright-coloring), the number of dyes should be as small as possible, generally not more than three, so as to facilitate the adjustment and control of the color light. At the same time, the components of the color-matching dyes (referred to as mixed dyes) should be understood, and as far as possible The dyes in the original components are used to supplement or adjust the color light to reduce the number of dyes used to ensure the brightness of the color and reduce the mutual conflict between the dyes.
3. "Fine tuning" principle
Shading adjustment is based on the theory of "afterglow". Therefore, the use of the principle of residual color to adjust the color light can only be a trace amount. If the amount is slightly more, the color will become darker, which will affect the vividness, and it will also affect the hue in severe cases.
4. The principle of "choose nearby" and "one complement and two complete"
When referring to color matching, whether it is the main color or auxiliary color dye, or the dye for adjusting color light, the dye closest to the target color should be selected, which is called the "closest selection" principle. At the same time, we should choose one dye as much as possible to obtain two or more effects, which is called the principle of "one complement and two complete".
If you want to fight emerald green, you should choose the green dye closest to emerald green if you can, and then choose the appropriate dye to adjust the shade according to your needs. You can also choose to mix emerald blue (green light blue) and tender yellow (green light yellow).
Another example is to fight red light blue, try not to use "blue + red", you should choose a color similar to blue (purple) to complement the red light, so as to "replenish nearby", so the operation of color matching is more convenient and economical.
color matching for dyeing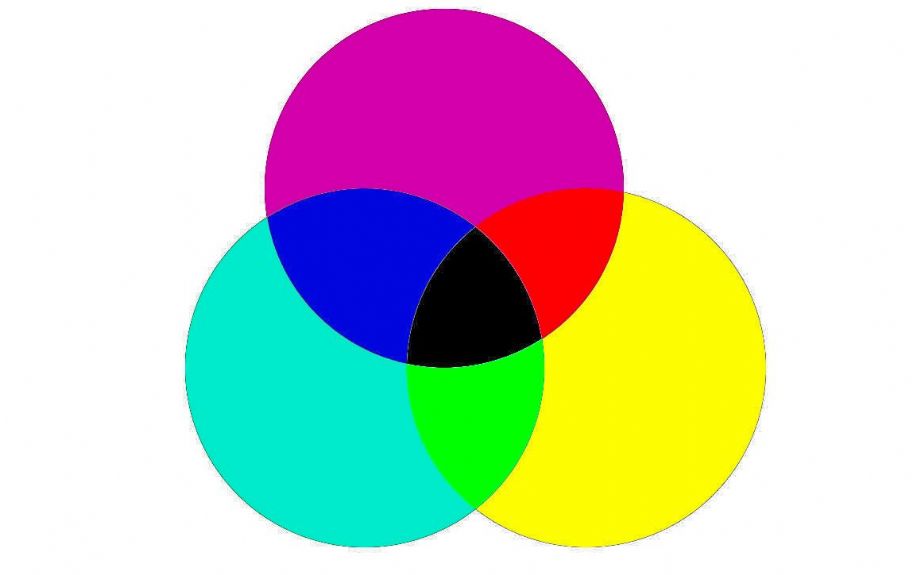
- Recommended Products:
- Sulphur Blue 13
- Sulphur Blue 7
- Sulphur Yellow 2
- Sulphur Red 14
- Vat Yellow 2
- Vat Blue 4
- Direct Red 23
- Direct Yellow 12
- Direct Yellow 11
- Direct Blue 15
- Acid Yellow 36
- Acid Yellow 17
- Acid Red 87
- Acid Red 18
- Acid Yellow 11
- Acid Blue 9
Products Catalog
- solvent red 24
- solvent red 49
- solvent red 122
- solvent red 111
- solvent red 146
- solvent red 195
- solvent yellow 21
- solvent yellow 33
- solvent yellow 93
- solvent yellow 98
- solvent yellow 114
- solvent orange 60
- vat red 41
- solvent green 3
- solvent green 5
- solvent blue 70
- solvent blue 104
- solvent black 3
- solvent violet 31
- solvent violet 13
Copyright right HANGHZOU EMPEROR CHEMICAL CO,,LTD © 2019 All rights reserved.

 Pусский
Pусский