Understand dyestuff knowledge, delivery problem
what about Application characteristics of solvent dyes in plastics coloring?
Solvent dyes are limited to the coloring of amorphous polymers (such as PS, ABS and other engineering plastics), because these polymers have high glass transition temperature. Under normal use conditions, such as room temperature (far lower glass transition temperature), the dyes will not migrate from the amorphous polymers. This is because in the dye polymer, the dye dissolves in the state polymer, the molecular movement of the dye is completely limited in the range of the polymer molecular chain, and there is no possibility for the dye to recrystallize or transport the polymer surface. Experiments show that if the polymer products colored with dye are placed in an environment with temperature higher than the temperature of the jar for a long time, the molecular movement of polymer molecular chain and dye molecule is no longer limited at this temperature, resulting in the transfer of dye. If the dye is used in some crystalline polymers (such as polyene smoke), because the glass transition temperature of these crystalline polymers is far lower than room temperature, the dye will migrate immediately.
glass transition temperature of some polymers
|
Polymer |
Glass transition temperature /℃ |
Polymer |
Glass transition temperature /℃ |
|
Glasses |
500〜700 |
PVC(Hard) |
80 |
|
PS |
98 〜100 |
PA6 |
60-70 |
|
SB/ |
80 〜105 |
PE |
-80 |
|
ABS/SAN PMMA |
105 |
PP |
3 |
|
PC |
143〜150 |
PP |
-5 |
Solubility
There is a common feature of solvent dyes used in plastic coloring, that is, they have good solubility in many plastics during processing, they form a stable solution in the processed plastic melt, the specific data of solvent dyes solubility in the polymer melt can not be obtained, however, it is possible to make an accurate evaluation. Because the solubility of solvent dyes in methacrylate and styrene is certain, but the solubility is very different from that in polar solvent ethanol.
Solubility of solvent dyes
|
Dyes |
Solubility(G/L) |
||
|
Methyl methacrylate |
Styrene |
Ethanol |
|
|
Solvent Yellow 160:1 |
2.4 |
4.7 |
0.3 |
|
Disperse Yellow 201 |
110 |
400 |
1.3 |
|
1.8 |
3.1 |
0.7 |
|
|
Solvent Yellow 130 |
0.1 |
0.2 |
<0.1 |
|
Solvent Orange 86 |
8.5 |
13 |
1 |
|
Disperse Orange 47 |
4 |
6 |
21 |
|
Solvent Red 111 |
7.5 |
13 |
0.7 |
|
Solvent Red179 |
1.6 |
4.5 |
0.1 |
|
Disperse Violet 31 |
35 |
25 |
1 |
|
Disperse Blue 97 |
18 |
55 |
<0.1 |
|
4 |
11 |
<0.1 |
|
|
Solvent Green 28 |
10 |
25 |
<0.1 |
Because solvent dyes are soluble in polymer melts, there is no dispersion problem in plastic coloring. The complete dissolution and uniform distribution of solvent dyes in polymer melts are necessary to avoid defects in the final product. In plastic colouring, uneven distribution of dyes in polymer melt will cause color lines, which must be avoided.
Solvent dyes are generally used to dye synthetic fibers before spinning by making them into masterbatch. Because the concentration of solvent dyes in masterbatch is relatively high, it is generally impossible to completely dissolve them in resin. If the mixed shear dispersion of masterbatch is not good during processing, it will also affect the spinnability, filtering performance and coloring performance of masterbatch.
Sublimation
When the solvent dye dissolves in the polymer, the physical phenomenon sublimation will occur. Sublimation refers to the phenomenon that the substance changes from solid state to gas state without experiencing liquid state with the increase of temperature. Different dye structures have different sublimation fastness. solvent red 111 is a typical example. It sublimates at the normal processing temperature of amorphous polymer. Different solvent dyes have different sublimation temperature.
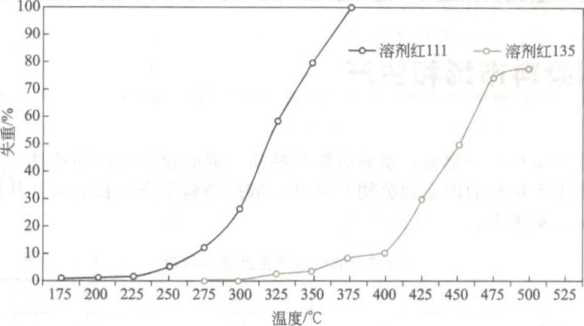
Although the sublimation of solvent red dye does not affect the colouring of plastics, it also affects the performance of solvent dye. When the colored polymer melt fills the mold at high temperature, part of the dye dissolved in the polymer melt changes into gas state, and deposits on the relatively cold mold surface, gradually forming more and more precipitates. If not removed in time, these deposits can cause defects on the surface of injection molded plastic parts. In theory, sublimation can be avoided by reducing the processing temperature, but in fact, it is impossible because each plastic forming process requires a certain processing temperature. The only way to avoid this is to use solvent dyes with good sublimation fastness.
Sublimation occurs not only in the process of plastic injection molding, but also in the process of resin drying and color masterbatch production, which will pollute the equipment, because it is necessary to dry before PA or pet coloring.
At present, more and more attention has been paid to the sublimation fastness of solvent dyes in plastics colouring. This is because the amount of dyes needed for coloring dark varieties has increased significantly, and the apparent defects of sublimation are larger. In addition, in order to increase the output, the temperature of plastics processing and molding has increased significantly (the influence of sublimation on rapid circulation, plastic injection hole and heat flow channel has increased), and the degree of production automation has increased (due to the mold structure and economic benefits) For economic reasons, it is impossible to clean the mold).
Melting point
The application of solvent dyes in plastic coloring is generally to process into color masterbatch, which requires relatively high processing temperature to accelerate its dissolution. Sufficient mixing shear is conducive to the uniform distribution of the melted or dissolved dyes in the polymer melt. The rapid distribution of melt dyes in polymer melts is very important, not only because there are great differences in the mixing of low viscosity melt dyes and high viscosity polymer, but also to avoid local supersaturation, which has a negative impact on the dissolution rate of dyes. The melting points of some solvent dyes are listed in table 5-6.
|
Dyes |
Burst point /P |
Dyes |
Melting point /P |
|
Solvent yellow 160:1 |
209 |
318 |
|
|
Disperse Yellow 201 |
115 |
Solvent Red 52 |
280 |
|
Solvent yellow 93 |
181 |
Disperse Violet 31 |
186 |
|
Disperse Yellow 54 |
264 |
Solvent Violet 13 |
189 |
|
Solvent yellow 130 |
300 |
Solvent Violet 36 |
213 |
|
230 |
Solvent Blue 97 |
200 |
|
|
Solvent Orange 86 |
180 |
Solvent Green3 |
213 |
|
Solven Red 179 |
255 |
Solvent Green 28 |
245 |
- Recommended Products:
- Solvent Violet 31
- Solvent orange 60
- Solvent yellow 114
- Solvent Yellow 93
- Solvent Red 135
- Solvent Red 111
Products Catalog
- solvent red 24
- solvent red 49
- solvent red 122
- solvent red 111
- solvent red 146
- solvent red 195
- solvent yellow 21
- solvent yellow 33
- solvent yellow 93
- solvent yellow 98
- solvent yellow 114
- solvent orange 60
- vat red 41
- solvent green 3
- solvent green 5
- solvent blue 70
- solvent blue 104
- solvent black 3
- solvent violet 31
- solvent violet 13
Copyright right HANGHZOU EMPEROR CHEMICAL CO,,LTD © 2019 All rights reserved.

 Pусский
Pусский